Link templates
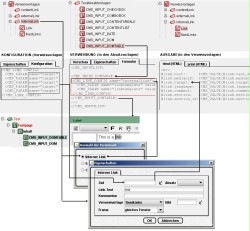
Template developers can use link templates for specifying the layout of links in detail within a FirstSpirit project. The editors enter all the necessary contents via a screen mask. Which fields can be filled in the screen mask depends on the configuration of the link templates.
All link templates are created within the "Link Templates" node in the Template Store. A differentiation is made between three Standard Link Types:
- externalLink: for external links, i.e. links to elements outside the project, for example to an external website.
- internalLink: for internal links to an element within the project.
- contentLink: for links to an element from the project's Content Store.
 |
genericLink: for generic link editors (from FirstSpirit Version 4.2). This type is excluded from the following documentation. For documentation about Generic Link Editors see separate subchapter. |
Any number of instances of the three types of link externalLink, internalLink and contentLink can be created below the "Link Templates" node. Each instance must have a unique name and correspond to one of the standard link types. An instance of each link type has been created in the figure. The instances are displayed in the tree display as folders.
New link templates can be created below the nodes of the link type instances (folders) (cf. Chap. Creating link templates).
The configuration of all link templates below the instance is defined via the instance. The link template is only used to define the output of the editorial contents.
The option of giving several instances of a link type enables different link configurations to be defined for different input components in the form area of a page or section template.
In this way, internal links, for example entered by the editor within the input component DOM Editor can be configured and displayed differently, for example, to links entered within the input component Link list (cf. Chapter Use in input components).
The following diagram is intended to more clearly illustrate the relationships between link templates and the maintenance of editorial contents.